Fruit Development
Enlargement of cluster & berries, tipping of the green shoots to archive uniform growth, remove weak growing shoots.
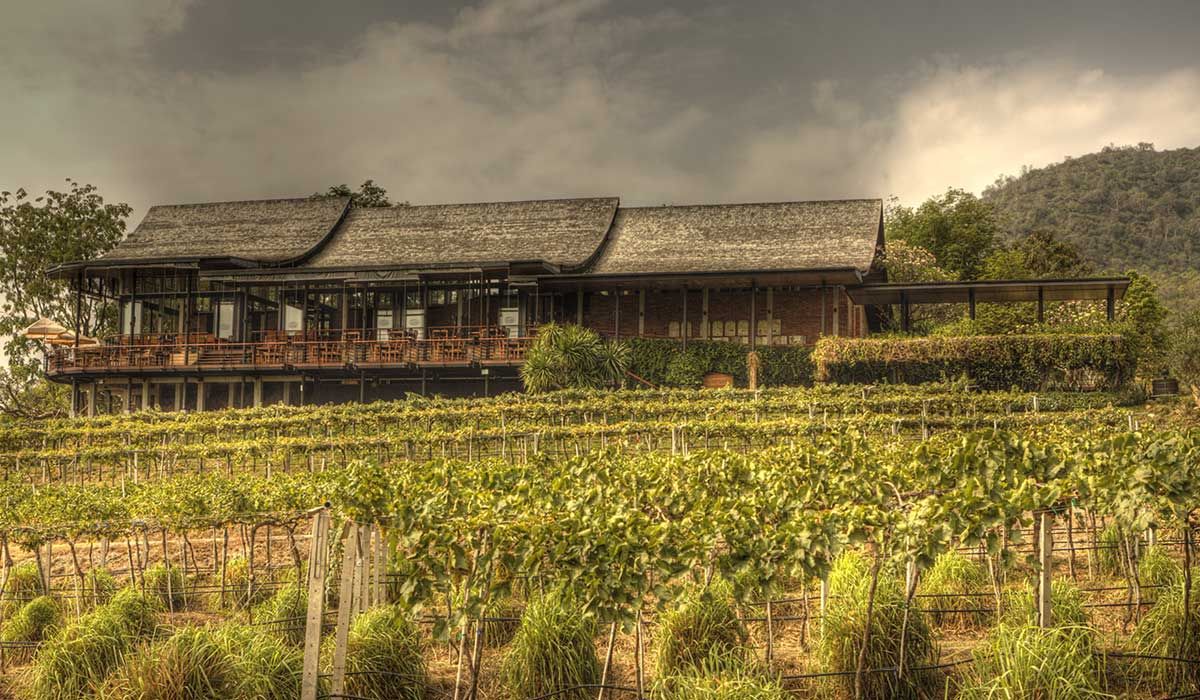

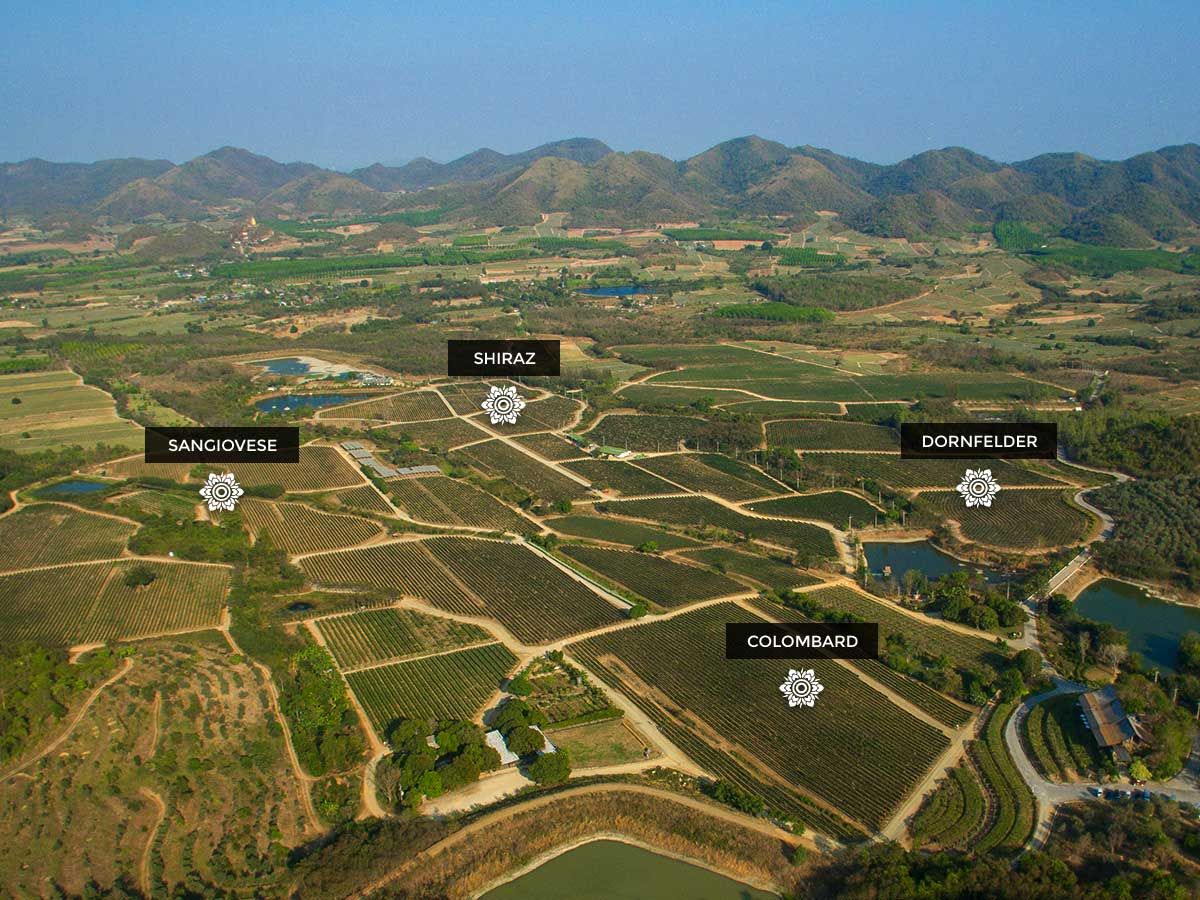
The grapes for Monsoon Valley Wines are grown in 3 locations: Monsoon Valley Vineyard at Hua Hin, Tab Kwang Vineyard and Chiang Mai Vineyard. Hua Hin Vineyard, the largest of the three, spans over 700 Rai (about 110 Hectare) of uncultivated land which will never be used for farming purposes and serve as a retreat for the local wildlife. Only rain water is what is used to keep the grapevines growing. During the rain-season, water gets collected in several ponds to irrigate the plants during the dry-season.

Within all vineyards itself, a certain biodiversity which is made up by insects is natural. Some of the insects can be harmful to the plants, the vermins. Other so called predators feed on the insects which have harmful effects to the grapes. Common pest control systems use chemicals which kill both vermins and predators – and sometimes also can be harmful to the environment. The Monsoon Valley Vineyards use Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus (NPV), a selective virus which is only harmful to certain insects. This way the vermins can be controlled while the predators and the environment don’t get affected.
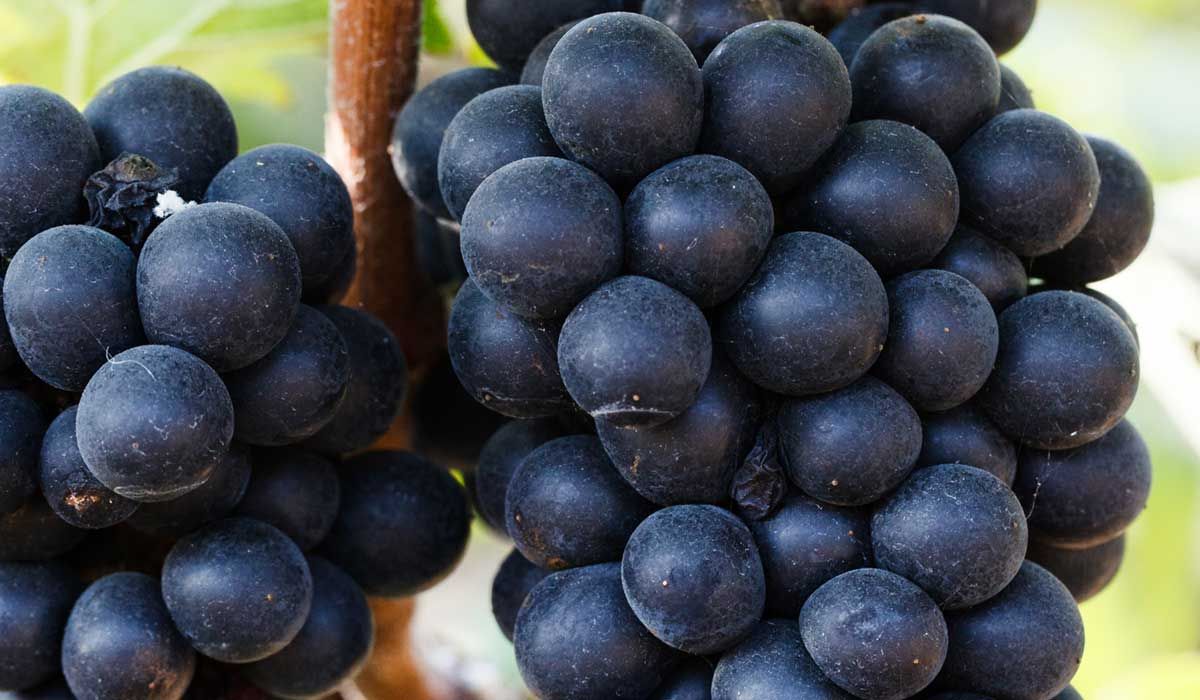

Also known as Syrah, is a French variety which has its origin in the Rhone-Valley in France. The myth that the variety originated from Persia (Todays Fars Province in Iran whose capital is called Shiraz) could be proven wrong.
Shiraz grapes have small, dark-blue berries with a currant-flavor. The plants love sunny and dry climate which makes them suitable to produce high-quality fruit during Thailand's dry-season. Depending on the region and the soil where the grapes are produced, Shiraz wines can develop a wide variety of flavors – this made the variety so popular that it has been elevated a group of ‘noble-vines’. Shiraz is mainly grown in France and Australia but also in California, Mexico, Argentina, South Africa and Italy – and it’s becoming more and more popular in tropical regions.

Jan
Fruit Development
Enlargement of cluster & berries, tipping of the green shoots to archive uniform growth, remove weak growing shoots.


Feb
Onset Of Rippenning
Represents the transition from berry growth to berry rippening, where color changes and skin softening; green harvest to reduce yield


Mar
Rippening & Harvesting
Sugar content increases, acidity balances, flavor & aroma development, then selective picking.


Apr
Short Prunning
Pruning 1 bud per spur


May
Bud Break
Sprouting of new shoots, shoot selection & distribution along cordon arm.


Jun
Canopy Management
Arrange shoots to exposure the light perfectly by using double wired trellis, carry out to minimize infestation & grant healthy development.


Jul
Canopy Management
Canopy management continues throughout July


Aug
Tipping
Control vegetative growth by frequent tipping which positively influrences the microclimate, good ventilation to avoid leave compaction.


Sep
Tipping
Controled growth by tipping continues throughout September.


Oct
Long Pruning
Pruning 3-4 bud pre spur.


Nov
Budbreak / Leave development
New shoot with grapes sprouting, shoot selective to avoid compact canopy.


Dec
Flowering
Blooming and Pollination, Defoliation along the grape zone "get more light into the vine"